Availability of Observing Capabilities in Cycle 20
During this cycle, the new Telescope Manager Specification System (TMSS) for specification and scheduling of LOFAR observations will be in use.
The capabilities of the telescope are split into two categories: available functionality during Cycle 20 and functionality that is not offered in Cycle 20. The capabilities are presented in the following table and described in more detail in the text following the table. It is followed by a section describing dynamic scheduling detailing essential requirements during the specification of the proposal.
It is important that you check the details regarding specification and scheduling (!) such that you are sure that your observing campaign can be executed. The details can be found below the table and on the separate web pages.
If you are unclear about the available functionality for your proposal, please contact Science Data Center Operations through the JIRA helpdesk [link]. For more detailed information about the observing modes, please follow this link.
| Functionality in Cycle 20 |
Not offered in Cycle 20 | |
| Number of beams | - Up to 8 | |
| Number of subbands | - Up to 488 | |
| Antenna modes | - LBA_OUTER
- LBA_SPARSE_EVEN - HBA_DUAL - HBA_DUAL_INNER - HBA_ONE - HBA_ZERO |
- LBA_INNER
- HBA_JOINED |
| Filters | - 10-90 MHz
- 30-90 MHz - 110-190 MHz |
- 170-230 MHz
- 210-250 MHz |
| Interferometric observing strategies | - Book-ended calibrator
- Parallel calibrator - LST distributed imaging(1) - Single target observation - Target followed by a calibrator |
- Parallel observations(1)
- Interleaved - Additional calibrator to book-ended strategy |
| Interferometric pipelines | - Preprocessing pipeline
- Demixing up to two sources - LINC (LTA post-processing pilot) (1) |
|
| Beamformed observing modes | - Multi-TAB (single pointing)
- Pulsar timing (complex voltage) - Fly's eye |
|
| Beamformed pipelines | - Pulsar Pipeline (PulP) | |
| Advanced and expert observing functionality | - Rapid Response mode
- Transient Buffer Board - AARTFAAC - Single station use in local mode during ILT time - Ingest of raw data from only one dataproduct of beamformed + imaging observation - Simultaneous beamformed + imaging(1) including a Solar mode - Dynamic spectrum toolkit(1) |
- Manual changes in the system, e.g. COBALT overrides
|
| Scheduling constraints | - Day/Night/Avoid Twilight
- Minimum elevation -Minimum distance from (Sun, Moon, Jupiter) - Offset from transit - Specific time or time ranges - Simple, independent cadence (e.g. Monthly) - Windfarm standstill time - More complicated cadences (e.g. day 1,2,5,10) - Availability of a specific set of stations (e.g. RS210, RS310, RS508, RS509) |
- Inter-observational constraints(1)
- Orbital constraints(2) |
(1) See explanation below
(2) Orbital constraints for binary systems are not modeled in the dynamic scheduler in cycle 20. The proposers should specify all available windows when requesting observations requiring a certain phase of a planet or a binary system.
Additional details on available functionality for Cycle 20
The HBA interferometric mode:
Observing strategies: T, C-T-C (default), T-C (where C=Calibrator, T=Target)
Free selection of subbands within the 110-190 MHz range, total bandwidth of up to 96 MHz, divided over up to 8 beams (recommendations here).
Pipeline: Preprocessing pipeline, demixing up to two sources, LINC (LTA post-processing pilot)
Antennaset: HBA_DUAL, HBA_DUAL_INNER, HBA_ONE, HBA_ZERO
Co-observing: We recommend users to co-observe with the LOFAR Two-metre Sky Survey (LoTSS) [link], if possible.
NOTE: The calibrator(s) will inherit the observing setup (e.g. antennaset, instrument filter, subband list, etc.) of the specified target observation.
The LBA interferometric mode:
Observing strategies: T||C (default), C-T-C (where C=Calibrator, T=Target, ||=in parallel)
Free selection of subbands within the 10-90 MHz range, total bandwidth of up to 96 MHz, divided over up to 8 beams (recommendations here).
Pipeline: Preprocessing pipeline, demixing up to two sources
Antennaset: LBA_OUTER, LBA_SPARSE_EVEN
Co-observing: We recommend users to co-observe with the LoLSS LBA survey project [link], if possible.
NOTE: The calibrator(s) will inherit the observing setup (e.g. antennaset, instrument filter, subband list, etc.) of the specified target observation.
The Pulsar Timing mode:
Complex voltage beamformed observation with a pipeline producing folded pulsar profiles for known pulsars. Available in the frequency range 10-90 MHz and 110-190 MHz.
Observing strategies: T (default). Default strategies available for Pulsar Timing, Scintillation, Fast Radio Bursts.
Antennaset: HBA_DUAL, HBA_DUAL_INNER, LBA_OUTER
Pipeline: Pulsar Pipeline for pulsar folding and/or to convert data to 8-bit
The Pulsar Search mode:
A beamformed observation with multiple tied-array beams in combination with incoherent array beams, in accordance to known limits. Free selection of subbands in the frequency range 10-90 MHz and 110-190 MHz.
Observing strategies: T (default). Default strategies available for RRATs.
Antennaset: HBA_DUAL, HBA_DUAL_INNER, LBA_OUTER
Pipeline: Pulsar Pipeline to convert data and to fold known pulsars
Transient Buffer Board raw voltage mode:
Direct storage of data from individual antennas.
The Rapid Response mode (Fast ToO) [link]:
An observation triggered automatically, within 5 minutes of the request. Observations are requested through a file uploaded by the user based on default templates available in the system.
NOTE: The calibrator(s) will inherit the observing setup (e.g. antennaset, instrument filter, subband list, etc.) of the specified target observation.
The Fly's eye mode:
A beamformed observation with each station recorded separately, but pointing in the same direction.
Antennaset: HBA_DUAL, HBA_DUAL_INNER, LBA_OUTER, LBA_SPARSE EVEN
Pipeline: Pulsar pipeline or Dynamic spectrum toolkit
LST distributed imaging (observing strategy):
In LBA, we have observed using 1 hour scans, spread over 3 non-continuous LST ranges. The LST offset window can be used to specify this. For each observation, the LST offset windows should be specified in the proposal. An LST offset window is specified as [start time, stop time] relative to a reference pointing (provided in the comments of the target list table in the proposal). Please allow for some flexibility when specifying the window, e.g., [-4 hr,-2.5hr] for a 1 hour observation.
Simultaneous beamformed + imaging observations
A few specific setups are available for simultaneous beamformed + imaging observations, see [link]
International Stations used in local mode during ILT time
It is possible to propose for International Station use in local mode during ILT time, if arrangements have been made with the International Station owners regarding the observing and processing of the data (see details here).
LINC pipeline
In Cycle 20 ASTRON-SDCO will run a pilot project for offering data processing service at the LTA. The pilot phase will be operated at SURFsara and the selected processing workflow is the LINC (v4). LINC is a set of pipelines (Calibrator, Target and Imaging) to correct for various instrumental and ionospheric effects in both LOFAR HBA and LBA observations. Proposals aiming at obtaining science with an HBA-NL array configuration are eligible for this pilot. For details see [here].
Dynamic spectrum toolkit
The user can request generation of quicklook plots and rebin the data to 0.011 second time resolution using the dynamic spectrum toolkit. It is not possible to request a cut-out of part of the data, as was possible in the past. Please specify in the proposal that you want to use the dynamic spectrum toolkit for your analysis.
Not offered in Cycles 20
- Antennasets: LBA_INNER, HBA_JOINED
- The high frequency filters: 170-230 MHz, 210-250 MHz
- Observing and processing setups that require editing of specifications outside of TMSS (e.g. COBALT correlator override)
- Parallel observations - multiple observations that run simultaneously using different stations, with the exception of the Solar beamformed + imaging mode.
Important considerations about dynamic scheduling
TMSS will dynamically schedule observations. All observing templates will be prepared before the start of the cycle and entered in the scheduling queue. They will then be scheduled automatically based on the constraints and the priority of the observations. The priority is set by scientific ranking, A/B queue and the target list ordering in the proposal.
If your observations should be performed following specific scheduling constraints, as usual you should clarify these in the appropriate field in the proposal. The requested constraints will be evaluated by the technical review panel.
In particular, in "Other observational constraints" specify whether observations should:
- Run during day-time, night-time or avoid sunrise/sunset
- Use a different minimum elevation than the default of 30 degrees for targets or calibrators
- Be observed offset from transit and by how much (e.g. obs1 [-4 to -2.5 hours], obs 2 [-0.75 to 0.75 hours], obs3 [2.5-4 hours] for sparse LST coverage imaging)
- In case of limited observing windows for example for observing phases of a binary system, specify all observing times. This can also be in the separate technical addendum if it doesn't fit.
- Be observed during windmill standstill time. For more information, see [link]
In general, the dynamic scheduler will determine the start time of the observations. However, observing at a specific start time or at an allowed range of start times can be specified, for simultaneous observing with other instruments.
Inter-observational constraints are restricted: Observations whose execution time depends on the schedule of other observations in the same cycle cannot be specified properly by the dynamic scheduler in Cycle 20 (e.g. a request to run an observation two days after another one). Proposers that have specific needs in this regard are advised to contact the SDCO group to further discuss options for Cycle 20. Regularly repeated observations on a weekly or monthly basis can be accommodated.
LST Availability during Cycle 20
This pages provides an overview of the available LST's for Cycle 20. This will guide proposers to properly design their observing campaigns. Note that this information is subject to change as:
- ToO triggers may reserve an LST range
- the system may become unavailable for other reasons (e.g. unplanned system/station maintenance, eVLBI observing sessions).
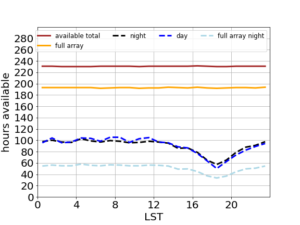
The plot shown above display the amount of observing hours available as a function of the Local Sidereal Time (LST). This plot shows total available time, available time with the full array and total night time and day time hours available, in red, yellow, black and blue, respectively for the full duration (one year) of Cycle 20.
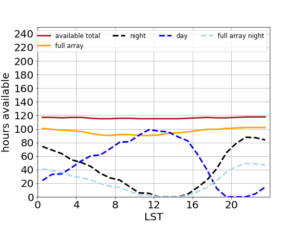
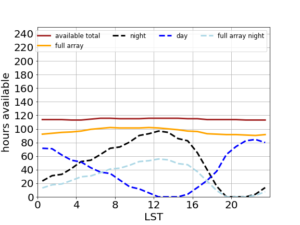
Proposers that need to request telescope time constrained to specific LST ranges with day-time/night-time observing can also check the LST availability in the periods June-December 2023 (left panel above) and December 2023-June 2024 (right panel above), in order to plan the needed observing campaign.
Please note that for e.g. an observing run of 8 hours centered at LST 05:00, time needs to be available from LST 1-9, or twice from LST 3-7 if it's split in two 4-hour blocks.
HBA Co-observing with the Surveys KSP team
To maximise the telescope efficiency the International LOFAR Telescope encourages PIs of standalone proposals to co-observe and co-process data with the LOFAR Two-Metre Sky Survey (LoTSS) team in HBA. This procedure is described in detail below, while in the following a summary of the main points is outlined.
- Any proposers interested in this opportunity should clearly state so in the technical section of their proposals.
- Before requesting LOFAR observing & processing time, proposers should check if the target of interest has been covered in any of the performed / planned pointings of the LoTSS by using the linked ALADIN interface.
- Any questions regarding HBA co-observing can be directed to lotss-admin@strw.leidenuniv.nl.
- Except in cases where tailored processing is required and a collaboration is formed between LoTSS members and the proposers, there will be no requirement for joint science analysis or publications and only an acknowledgement will be required in any resulting publications.
- HBA co-observing consist of requesting LOFAR observing & processing time in multi-beam mode to observe two pointings simultaneously, allowing one to be used by the proposer and the other by the LoTSS team.
- Each pointing is observed with the full LOFAR array, with almost contiguous frequency coverage from 120-168MHz and an integration time of 8hrs.
- The desired target of the proposer can be observed either by observing the closest pointing on the SKSP grid or by observing directly at the target. In both cases, the second beam will be placed on the LoTSS grid.
- As a result of the collaboration the LoTSS team will provide proposers with:
- assistance with the preparation for observations with the observatory;
- within a period of 4 weeks (except in exceptional circumstances) the products from the standard direction independent calibration pipeline (for the quality of the images that can be produced from these data see Shimwell et al. 2017, A&A, 598, A104) in addition to the regular data products provided by the observatory;
- if both pointings are placed on the LoTSS grid, within 8 weeks of the observations, the LoTSS team will also run the standard surveys direction dependent calibration and imaging pipeline and provide the user with the resulting images. If either pointing is not placed on the LoTSS grid this pipeline will be run on a best efforts basis;
- if additional, more tailored, processing is still required to produce science quality images, the LoTSS team will be open to discussion of a collaboration with the proposers on the data processing in an attempt to help provide science quality images.
RATIONALE
Before requesting LOFAR observing & processing time, proposers must check the presence of any data in the Long Term Archive that may fit their science goals. In particular, proposers that are interested in interferometric data are also requested to check if the target of interest has been covered in any of the performed / planned pointings of the LoTSS. If so, proposers are encouraged to collaborate with the LoTSS team in order to have access to the processed data by contacting lotss-admin@strw.leidenuniv.nl. Otherwise proposers can review the sections detailed below and contact the LoTSS team, in order to co-observe in a multi-beam mode. To this aim, PIs will first need to check with the LoTSS team if any survey pointing can be selected around the target of interest.
In order to verify either if:
- any of the performed / planned pointings of the LoTSS survey is available to cover target of interest,
- any survey pointing can be selected around the target of interest
proposers can use the ALADIN interface linked below, which shows the progress with the survey (red unobserved, blue observed and yellow is planned for the upcoming observing cycle). By clicking on the centre a popup window will list details about the selected pointing. Furthermore, details of all observed LoTSS pointings are summarized in a table.
OBSERVATIONAL AND PROCESSING DETAILS
The LoTSS team is aiming to observe the entire Northern sky with 3168 pointings above declination 0 as described in Shimwell et al. 2017, A&A, 598, A104. Each pointing is observed with almost contiguous frequency coverage from 120-168MHz and an integration time of 8hrs. The separation between LoTSS pointings is typically 2.6 degrees implying that every target above declination 0 is contained (well) within the primary beam of a LoTSS pointing. To facilitate HBA co-observing the LoTSS project is using 8-bit mode and exploiting the multi-beam capability of LOFAR to observe two pointings simultaneously, allowing one to be used by the proposer and the other by the LoTSS team. To co-observe with LoTSS the desired target can be observed either by observing the closest pointing on the SKSP grid (this is the preferred option) or if the source is sufficiently far from any LoTSS pointing centre that sensitivity loss becomes important, by observing directly at the target and placing the second beam on the LoTSS grid.
A summary of the LoTSS setup, which must also be adopted for any HBA co-observing project is given below:
- an HBA Dual Inner, 8 hours long (split in multiple observations at low-declination if necessary) observation which is book-ended with 10 min flux calibrators;
- the full (CS,RS,IS) LOFAR array is used;
- the bandwidth for each pointing (at least one on the LoTSS grid) is 243 subbands and one subband is used to centre the tile beam between the two observed paintings.
- the data will be averaged to 16 channels per subband and 1 secs.
As a result of the collaboration:
- the LoTSS team will provide standard text detailing the data processing that has been performed and text describing the observation setup for the technical case of a proposal (see https://lofar-surveys.org/co-observing.html);
- the LoTSS team will assist the proposer with the preparation for observations with the observatory;
- within a period of 4 weeks (except in exceptional circumstances) the LoTSS team will send the PI of the HBA co-observing proposal the products from the standard direction independent calibration pipeline (https://github.com/lofar-astron/LINC) in addition to the regular data products provided by the observatory. This calibration is for the Dutch stations only and international stations are removed from the calibrated datasets. The quality of the images that can be produced from these data without any further calibration is detailed in Shimwell et al. 2017, A&A, 598, A104;
- many science cases will require higher quality images that can only be obtained with some form of direction dependent calibration. Therefore if both pointings are placed on the LoTSS grid, within 8 weeks of the observations, the LoTSS team will run the standard surveys direction dependent calibration and imaging pipeline (https://github.com/mhardcastle/ddf-pipeline) and provide the user with the resulting images. If either pointing is not placed on the LoTSS grid this pipeline will be run on a best efforts basis. The quality of the images produced by the standard surveys pipeline will be detailed in a forthcoming article but typically the sensitivity achieved, at optimal declinations, is 0.1mJy/beam at a resolution of 6arcsec. However, there are significant variations depending on the ionospheric conditions, the source environment and target declination;
- if additional, more tailored, processing is still required to produce science quality images, the LoTSS team will be open to discussion of a collaboration with the proposers on the data processing in an attempt to help provide science quality images.
Except in cases where tailored processing is required and a collaboration is formed between LoTSS members and the proposers, there will be no requirement for joint science analysis or publications and only an acknowledgement will be required in any resulting publications.
POLICY
- After the ILT PC meeting, the PIs of successful proposals who have expressed an interest in the aforementioned opportunity will be placed in contact with the Surveys KSP team, who will select (if available) the LoTSS pointing to be observed in parallel with the PIs target.
- If awarded observing & processing time, the HBA co-observing project will run with the same observing and processing setups as adopted by the LoTSS team.
- Data will be recorded and archived under the HBA co-observing project; both that project and LoTSS teams will have simultaneous proprietary access to data placed into the LTA as processed by the ASTRON.
- The observing hours will be accounted to the allocation of the HBA co-observing project.
- The ILT-PC is the final authority for stipulating science use rights and limitations, proprietary time (default 1 year), etc.; PIs should ensure that any requests they have in this regard are justified in their proposal.
- The acknowledgments required on any publications resulting from HBA co-observing projects can be found on https://lofar-surveys.org/co-observing.html
LBA Co-observing strategy
Due to the rapid improvement of the LBA imaging techniques, in Cycle 20 we give the possibility for PIs of standalone proposals, who are interested in exploiting the LBA imaging capabilities of LOFAR, to co-observe and co-process data in shared-risk mode with the LOFAR LBA Sky Survey (LoLSS) team. The LOFAR LBA Sky Survey aims to cover the entire northern sky down to the sensitivity of 1 mJy and the resolution of 15 arcsec. Here we summarize the procedure to follow to adopt this option:
- Any proposer interested in co-observing should contact the coordinator of the LBA Sky Survey well in advance before the proposal deadline (contact: Francesco de Gasperin) to discuss whether a Co-observing strategy would be mutually beneficial. The LBA Survey coordinator will decide if the project for which he is approached would make mutual sense to do as co-observing. Note that we have limited experience on observations pointed on the galactic plane.
- Any of the selected proposers should clearly state so in the technical section of their proposals.
- Co-observing consists of requesting LOFAR observing and processing time in multi-beam mode to observe four pointings simultaneously, allowing one to be on the calibrator, one to be used by the proposer, and two on nearby survey fields.
The benefits of co-observing with the LBA Survey are:
- The LBA survey team will assist the PI in preparing the technical part of the proposal providing a standard text detailing the observation setup.
- The LBA survey team will assist the proposer to check the observation setup in TMSS.
- The processing of the calibrator and of the target up and including the direction independent calibration will be taken care of by the LBA survey team. The intention is that calibrated visibilities and images will be made available 4-8 weeks after the observations.
- The LBA survey team will provide standard text detailing the data processing that has been performed to be included in publications.
Characteristics of the final products:
- Each pointing is observed with the full dutch array.
- The frequency coverage is contiguous in the range 42-66 MHz (mid frequency: 54 MHz).
- The total integration time should be a minimum of 4 hours or a multiple of 4 hours.
- The time resolution is 2 sec, the frequency resolution is 4 ch/SB (0.049 MHz).
- The direction independent calibrated image will have ~3 mJy/psf rms noise and ~45" resolution. Consider however that due to the ultra-low frequencies, substantial direction dependent errors will decrease the image fidelity.
- The process to obtain a full direction dependent calibrated image is possible but it is still experimental and it is not provided as part of the co-observing mode, however it may be conducted on a best effort basis upon agreement with the survey coordinator. Currently, we were able to reach an rms noise of ~1-1.5 mJy/psf and a resolution of 15" in a few testing fields. The presence of some errors in the vicinity of bright sources (>1 Jy @ 54 MHz) is expected.
Policies:
- After the ILT PC meeting, the PIs of successful proposals who were selected for co-observing will be put in contact with the LBA Survey Coordinator for the necessary project preparations. If awarded observing and processing time, the co-observing project will run with the same observing and processing setups as adopted by the LBA Survey team.
- Data will be recorded and archived under the co-observing project; both that project and LBA Survey teams will have simultaneous proprietary access to data placed into the LTA as processed by ASTRON.
- The observing/processing hours will be accounted to the allocation of the co-observing project.
- The ILT-PC is the final authority for stipulating science use rights and limitations, proprietary time (default 1 year), etc.; PIs should ensure that any requests they have in this regard are justified in their proposal.
Example of DIE calibrated image:
Example of DDE calibrated image:
ORP Transnational Access Programme
Several proposals are eligible for the Transnational Access (TA) programme of ORP (Opticon RadioNet Pilot project).
ORP is a project supported by the European Commission (EC), which brings together the premier radio astronomical facilities in Europe to serve a growing research community across all of Europe and beyond. Building on national investments and commitments to operate these facilities, this specific EC programme leverages the capabilities on a European scale.
Transnational Access offers free of charge, merit-based, access to the European telescopes or arrays, such as EVN, e-MERLIN, IRAM-NOEMA, IRAM-PV, LOFAR, Effelsberg, APEX, SRT, and ARC Nodes. Access to these infrastructures or installations includes the professional user support on the technical and scientific level.
Access to the ILT
For the ILT, the TA programme contributes towards the operational cost of eligible projects, thus allowing a larger number of projects to be carried on.
In addition, travel subsidies for TA users to visit the ILT's operational centre at ASTRON and analyse their data with the help of experts, can be supported by ORP.
A request for support of travel costs is to be submitted to the ORP TA leader of the facility at the email address: pizzo@astron.nl.
Eligibility
The TA programme offers access to the ORP facilities for users working in European and also non-European institutes (the latter case has some limitations).
Traditionally an eligible research team (TA Users) is comprised of all co-authors in an observing proposal where:
- The PI is from an institute in a country of the EU or Associated States (AS), with the exception of the Netherlands.
- The same criterion, but applied collectively to 50% or more of the individual members of the research team.
- With some limitations, projects with PI and the majority of the team from non-EU or AS could be accepted
Terms and Conditions for TA Users to comply to
Eligible groups will be notified though the Programme Committee feedback.
Groups that wish to apply for travel grants should follow the procedure above.
As recipient of support from EC, the TA user, need to commit to the following:
| Project Summary | The TA user need to fills in a project summary including personal information (e.g. name, gender, nationality) and authorises EC to publish this information for statistical purposes. |
| Publications | TA users are expected to disseminates the generated results, in the form of scientific publications and
- acknowledge ORP support by including in their publication: The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 01004719 [ORP] - inform the ORP TA leader about the resulted publications |
| User questionnaire | Feedback from the TA users is vital for documenting the importance of the TA-supported facilities to the EC and for improving the ORP TA programme.
TA user should fills in the form on https://ec.europa.eu/eusurvey/runner/RIsurveyUSERS ATTENTION: o Acronym of the EC Grant: 01004719 ORP o User Project Acronym: name of the TA proposal o Answer to the question No 5: No AND send a confirmation of the questionnaire submission to RadioNet@mpifr.de |
Observing in single-station mode
Use of international stations in single-station mode during ILT time
For proposals requesting the use of the international stations in single-station mode during ILT time, it is the PI’s responsibility to verify – before submitting the proposal - that local resources are available to run such projects at the international stations. In its deliberations, the LOFAR Programme Committee will assume that the submission of such projects is indication that local resources will be available to accommodate it.
The get in contact with the international station managers to verify the availability of local resources to run your project, please use the information below:
DE601: O. Wucknitz wucknitz[at]mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
DE602: B.Ciardi, ciardi[at]mpa-garching.mpg.de
DE603: M. Hoeft, hoeft[at]tls-tautenburg.de
DE604: C. Vocks, lofar-ops[at]aip.de
DE605: B. Adebahr, adebahr[at]astro.rub.de lofar-ops[at]astro.rub.de
FR606: J. M. Griessmeier, lofar-ops[at]obs-nancay.fr
SE607: T. Carozzi, tobia[at]chalmers.se lofar-ops[at]chalmers.se
UK608: M. Hardcastle, m.j.hardcastle[at]herts.ac.uk lofar-ops[at]stfc.ac.uk
DE609: J. Kuensemoeller, jkuensem[at]physik.uni-bielefeld.de lofar-ops[at]physik.uni-bielefeld.de
PL610: Hanna Rothkaehl, hrot[at]cbk.waw.pl
PL611: Marian Soida, soida[at]oa.uj.edu.pl
PL612: Leszek Blaszkiewicz, leszekb[at]matman.uwm.edu.pl
IE613: Evan Keane, evan.keane[at]tcd.ie
LV614: R. Pauliks, romass[at]venta.lv
Pilot LINC Pipeline Cycle 20
In Cycle 20, ASTRON-SDCO will run a pilot project to offer data processing service at the LTA. The pilot phase will be operated at SURFsara and the selected processing workflow is the LINC (v4). LINC is a set of pipelines (Calibrator, Target and Imaging) to correct for various instrumental and ionospheric effects in both LOFAR HBA and LBA observations, as detailed in here.
Following the standard pre-processing step performed by ASTRON, direction-independent calibration can be performed using the LINC pipelines. Major changes for the current release (v4, September 2021) are:
- change of pipeline framework from “generic pipeline” to CWL
- optimization of the available algorithms (demix and clipping) for the mitigation of the presence of bright off-axis sources.
It includes:
- removal of clock offsets between core and remote stations (using clock-TEC separation)
- correction of the polarization alignment between XX and YY
- robust time-independent bandpass correction
- ionospheric RM corrections with RMextract
- removal of the element beam
- advanced flagging and interpolation of bad data
- mitigation of broad-band RFI and bad stations
- direction-independent phase correction of the target, using a global sky model from TGSS ADR or the new Global Sky Model (GSM) for HBA and LBA data, respectively.
- detailed diagnostics (and soon a summary log file)
How to / who can apply
Proposals aiming at obtaining science with an HBA (Dutch or full) array configuration are eligible for this pilot. Users' requests can be specified in the proposal technical justification section. For this users should specify the averaging (frequency/time) factors for the output target data products.
A selection of the submitted projects will be done by the technical panel; if selected and approved by the LOFAR Proposal Committee (PC), the contact author and the PI of the project will be informed via the PC feedback.
Data products delivered to the user
LINC data products that are made available to the user are:
- Calibrated uv Measurement Sets
- Calibration solutions collected in H5parm files
- Diagnostic plots (and soon a summary log file)
- Diagnostic Stokes I/V full bandwidth and wide-field FITS image
All final data products will be stored at the LOFAR Long Term Archive. Users can retrieve datasets from the LTA for reduction and analysis on their own computing resources or through the use of suitable resources on the GRID.
Below we summarise key diagnostics of HBA pipeline products in the image plane as obtained by inspecting a set of test fields processed via LINC v3. The expected quality for LINC v4 is expected to be comparable (or greater). The table shows the range of diagnostic values obtained for the different fields. The data were recorded with typical interferometric setup:
- antenna mode:HBA dual inner array
- instrument filter:110-190 MHz
- time averaging factor:1
- frequency resolution:8 channels/subband
- observation duration:4-8 hr
| PARAMETER | NOTE | HBA (110-190 MHz) |
| Glat [deg] | No trend with Galactic latitude has been found for any of the diagnostics. | 0.3-72.2 |
| Distance to closest A-team source [deg] | The synthesised beam was found to be highly elliptical for some fields due to missing remote stations and/or a high amount of flagged data at the high end of the band. | 10-33 |
| Bmaj/Bmin | 1.39-2.32 | |
| Median LOFAR/TGSS flux | 0.89-1.29 | |
| Mean RA separation (LOFAR - TGSS) [arcsec] | -1.6 to 0.3 | |
| Mean Dec separation (LOFAR - TGSS) [arcsec] | 0.1 to 0.8 | |
| Median inband (120-187 MHz) spectral index | The bandwidth was divided into 6 sub-bands. The spectral indices tend to be closer to -0.8 when discarding the highest-frequency sub-band (162-187 MHz). | -1.53 to 0.56 |
| ****RMS noise (within the main beam) [mJy/bm] | The median RMS values for the test fields have been obtained from the RMS noise maps. Note that dynamic ranges of the order of 3500-20000 can be reached from the measured RMS values. | 0.5-0.9 |
| *****Reliability [%] | The reliability is estimated as 1.0 - Nneg / Npos, where Npos is the number of sources detected above 5 sigma and Nneg is the number of negative peaks < -5 sigma; this calculation assumes that the noise distribution is symmetric about zero. | 98.5-99.8 |
Documentation
Documentation of the LINC pipeline is available on line:
- Overview paper describing the calibration strategy of the workflow(s)
- Full pipeline documentation can be found here. See calibrator, target and imaging pipelines sections for more details.
The aforementioned available full documentation refers to LINC (v4).