General User Administration
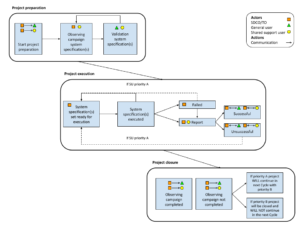
Figure 1: Diagram shows the three phases of the science project administration workflow (project preparation, project execution and project closure) along with the main steps. Actors and their responsibilities are indicated with the symbols. See table below for details.
Acronyms: SDCO - Science Data Center and Operations; TO - Telescope Operators; PC - Program Committee; SU - Scheduling Units; QA - Quality Assurance; TMSS - Telescope Manager System Specification; MoM - Management of Measurements
| Process steps | SDCO | General user | User shared support mode |
| Contact author is notified via Jira about the project preparation | SDCO will open a ticket in Jira to be used as the communication channel for the science project between the contact author and SDCO | The science project contact author will be responsible for providing any additional / missing info requested for the preparation of the observing campaign as well as for the acceptance of the delivered data. See here for instructions on how to use Jira. | |
| User specification (via the proposal in NorthStar) is converted / imported into TMSS | SDCO will rely on the info gathered from the proposal as well as from the feedback given by the PC and technical teams | The expert user(s) will rely on the info gathered from the proposal as well as from the feedback given by the PC and technical teams | |
| Check if any changes are needed to the proposed scheduling set; when ready the project status in TMSS is set to active | SDCO collect info for later reporting.
SDCO applies changes when needed if matching the allocated resources. SDCO/TO Change the status in TMSS |
The contact author will validate the specification in TMSS (follow the instructions in the section below) of the observing campaign and contact SDCO via the Jira ticket. | The expert user(s) will validate the specification in TMSS for the observing campaign and contact SDCO via the Jira ticket
SDCO/TO Change the status in TMSS |
| The set of SU is approved for (dynamic) scheduling. | TO/SDCO Change of status in TMSS | TO/User Change the status in TMSS |
|
| SU performed successfully & User accept data |
|
Contact author receives notification (email / Jira) and as soon as possible provide feedback (please find here some instructions on how to assess the data quality) |
|
| SU successful & User does not accept data |
|
Contact author receives notification (email / Jira) and as soon as possible provides feedback. Note that rejection of data must happen within 4 weeks from the data delivery in the Long Term Archive (LTA) in order to apply for a repetition. |
|
| SU failed |
|
Contact author receives notification (email / Jira). Note that in some cases the science team may find the data acceptable and in such cases should contact ASAP via Jira SDCO. |
|
| Closure of the project: prio A all SU performed & successful | SDCO closes the Jira ticket and the changes the status in TMSS into finished and report | ||
| Closure of the project: prio A part of SU performed successful | SDCO closes the Jira ticket and the changes the status in TMSS into suspended and report. | ||
| Closure of the project: prio B part of SU leftover. | SDCO closes the Jira ticket and the changes the status in TMSS into finished and report. |
Shared-Support Workflow and Duties
For the Shared-Support workflow as well as documentation for the day to day duties of the Shared-Support user, please see below.
1. Preparing Observations in TMSS
Please consult the TMSS User Manual on how to specify the proposed observation by setting up the appropriate Scheduling Units and associated processing tasks for a given Project.
2. Checking Observations & Pipelines
Data quality assessments for completed observations are performed to ensure the observations are acceptable within the LOFAR data policy. Before assessing the observations, ensure the observation cannot be considered failed (the criteria for a failed observation is outlined in the LOFAR data policy). If this is the case, the following assessment can be skipped and the procedure for failed observations described below should be followed.
The data quality assessment is done using a variety of tools that help assess the data at various stages along the data flow from the station. Most of the diagnostic tools are found on the inspection plot page of the observation here. To check the observations select the SAS ID of the observation for which you wish to inspect. A page will open, containing the following diagnostic information:
- COBALT error log: reports any errors during the processing and recording in the correlator of the data stream.
- Input loss report: reports the data loss from each station (if any).
- Station dynamic spectra: shows the signal power at each station as a function of time and frequency. The core, remote and international station dynamic spectra are shown and can be used to check and report any unusual features in the station behaviour (such as RFI, presence of bright off-axis sources in the station beam and its sidelobes, oscillating tiles, etc.). For a detailed description of different features on individual inspection plots, see the What do I see here? page.
- Visibility amplitudes plots: these are listed under the station dynamic spectra with format eg. SAP000 SB000. Each link shows the visibility amplitudes as a function of time for each individual subbands (frequency). From the displayed plots the behaviour as a function of frequency in the bandwidth of the observation can be checked. The different colour lines you see in the plots are relative to 4 signal combinations xx=dark blue, yy=red, xy=light blue, yx=pink. For an unpolarised source, xy and yx should be zero (within the noise), while xx and yy will contain the signals. Note that these plots are available for interferometric observations only. For a detailed description of the individual inspection plots, select the What do I see here? link.
In case of a failed observation (the criteria for a failed observation is outlined in the LOFAR data policy), the expert-user must mark the failure on the google schedule, notify the SDCO team and report the failure:
- Mark the observation as failed on the google schedule.
- Since the data is automatically ingested by TMSS, notify the SDCO team through the project Jira ticket with the SASID so that they can remove it from the LTA.
- Navigate to the LOFAR Observing Failures form and log the failure.
3. Writing Data Quality Reports
After checking the observations using the steps above, the Data Quality Report needs to be written.
- Firstly, select the report template JIRA by selecting CANNED RESPONSES > BLANK OBS REPORT in the format bar of the text box. (If CANNED RESPONSES is not available see template at end of section)
- State which observations are successful/failed. (The criteria for a failed observation is outlined in the LOFAR observing policy.)
- Add the general notes i.e. comments that apply to all observations/stations.
- Copy & paste the observation(s) row(s) from the inspection plots page to the Observations section.
- Add the completeness of the data.
- Add the performance of the system. For each observation, list the unusual features of the stations spotted when checking the observations.
- Add the status of the data recording, data processing and archiving.
- Finally, add remarks or specific actions required.