This document aims to provide a succinct overview of various aspects of LOFAR, supplemented by links to external, more detailed information. It is specifically aimed at new users, but contains information relevant for all users of LOFAR. Any suggestions, improvements or comments can be submitted to the ASTRON SDCO helpdesk ticketing system.
What is LOFAR?
LOFAR (LOw Frequency ARray) is an international telescope operated by ASTRON spanning several countries, including the Netherlands, France, Germany, Ireland, Latvia, Poland, Sweden and the UK, currently comprising 52 individual stations. There are two types of antennas at each station: the High Band Antennas (HBA, 110-240 MHz) and Low Band Antennas (LBA, 10-90 MHz). In total more than 8,000 antennas spread across the continent.
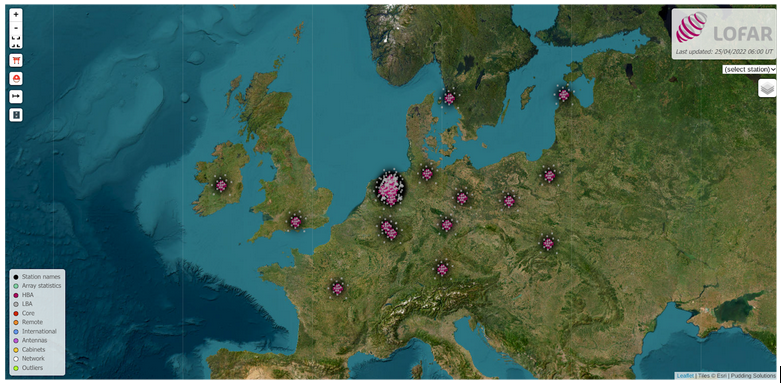
See here for an interactive version of this map
How is LOFAR operated?
ASTRON manages and operates LOFAR, in conjunction with collaborators at the international stations. The ASTRON Science Data Center Operations (SDCO) team is responsible for user assistance, technical assessment, observation preparation, oversight of pipelines/ingest/data processing and system tests. SDCO liaises with the Telescope and Operations (TO) team (who carry out observing from ASTRON) and Maintenance team, as well as Software Delivery (SD) team who manage and develop all software associated with the operation of LOFAR. If you have questions about anything LOFAR-related, your first point of call should be the SDCO team by submitting a support request via the SDC helpdesk ticketing system.
What kind of science does LOFAR produce?
LOFAR is used to carry out a wide range of scientific investigations, including six Key Science Projects. LOFAR scientific results are presented to the community through conferences, status meetings and schools, with a list of LOFAR papers archived here. A wealth of informative presentation slides can be found in the LOFAR Slide Repository.
Where can I find info about the current status of LOFAR?
Detailed system information about LOFAR (including stations, antennas) and other technical information can be found here. For information and insight into the current status, see here. A series of LOFAR newsletters, released every few months, also provide up to date information about LOFAR. It is also recommended to subscribe to the LOFAR news mailing list to be emailed updates about LOFAR. LOFAR Status Meetings for regular updates are held monthly, with presentations and recordings archived on LOFAR Slide Repository. Stop days, roll-outs and proposal deadlines, as well as other events, can be found listed on the LOFAR Google Calendar. Current known system issues are listed here.
What different observing modes are there for LOFAR?
LOFAR telescope is a responsive system that can react within 5 minutes from a triggered event. Details can be found here. Observations can take place using all stations, or a subset of the available stations (e.g. Core, Remote, International), with the HBA or LBA components of each station. The major observing modes include interferometric, beam-formed, commensal and direct storage, which are described in more detail here. There are experts in each of these different types of observing modes within the SDCO team, so you are advised to contact SDCO for more details if necessary. Of consideration also should be the angular resolution and sensitivity capabilities, in alignment with a given science case. An overview of the offered telescope capabilities and services is available here.
How do I propose observations with LOFAR?
There are observing cycles each spanning 6 months, starting in December and June each year. You can find out more about how to submit a proposal here. Proposals are submitted through the NorthStar tool. You will need to create a user account to access this web tool. All Cycle allocations, including the current cycle, are archived here.
How do I plan for proposed observations?
SDCO offers a set of LOFAR tools which can be used to help plan for observations during a given Cycle. These include LOFAR calculators for estimating sensitivity, frequencies and source visibility. Info about the specification, the scheduling and project administration is also available here. It is also recommended to check the current issues page.
My data has been observed, what do I need to do as a PI before it is archived?
An email will be sent to you by SDCO upon the completion of your observations, with details about any issues you may expect with the data. Upon receipt of the email, you are given a 24-hr period to assess the inspection plots of the observations and decide whether the data quality is sufficient to proceed with ingesting into the archive.
Where can I store and process my data?
Your submitted proposal should contain details of your storage/processing requirements from the SDCO. All SDCO processing pipelines are carried out on the CEP4 supercomputing cluster after observations. The Long Term Archive (with sites in Amsterdam, Juelich and Poznan) provides indefinite tape storage for LOFAR data products produced by the CEP4 processing pipelines, which are accessible publicly after a 1 year proprietary period. A processing service for generating high level data products will be available soon. Users interested can contact SDCO via the helpdesk.
I am having trouble with some LOFAR-related software, what should I do?
If the tool listed is one of those listed here, it is recommended that you first try to contact the owner/manager of the software tool, or open an issue on the related Github page. If it is software that is managed by the SDCO/SD (e.g. the standard processing pipeline), then you may contact the SDCO team by submitting a support request to the SDCO helpdesk. Note: SDCO can provide limited support on a best-effort basis for third-party software and user scripts.
What kind of pipelines are run on the data before I receive it?
The SDCO team in combination with the TO team will pre-process observations at a basic level, but will expand soon to include advanced direction (in-)dependent pipelines. You can read more about the pipelines currently supported by ASTRON here.
Are there any cookbooks or tutorials I can use for reducing my data?
There is an official LOFAR Imaging Cookbook, including tutorials, which is the best place to start for imaging a LOFAR observation. A LOFAR Beam-formed Cookbook is currently in development. Beam-formed data can be analysed with standard pulsar packages like psrchive and dspsr, or using the LOFAR dynspec tools. You can find all available cookbooks here. We also recommend for new users to attend a LOFAR School for a detailed introduction into observing with LOFAR and using LOFAR data. Schools are organised with a two year cadence. Users can also contact SDCO to plan a visit to ASTRON for having dedicated support for data processing.
I have an awesome result using LOFAR data - who should I contact?
If you have a press release coming out which incorporates LOFAR data, please contact the ASTRON Communication team. Support may also be available for constructing a news article or press release through ASTRON, depending on the nature of the result. Any published article using LOFAR data should appear soon after on the LOFAR Science Paper list, but if you do not see your paper there after a few months, please contact the SDCO team. Authors are also requested to add the official LOFAR acknowledgement to their publications. You may also consider submitting an ASTRON/JIVE Daily Image. You are also welcome to publicise relevant daily activities and photos on Twitter, tagging ASTRON and LOFAR.
Is there one single place to find a detailed overview of LOFAR?
The best places to get a detailed insight are the LOFAR book and the paper by van Haarlem et al. (2013). Some information may be outdated since the publication of these references, so for the latest status you are referred to the online pages.
Where can I find information about the LOFAR policies regarding data quality/storage/authorship?
Information about LOFAR policies can be found on the relevant section of the online webpages. These include information about what quality is deemed sufficient by the SDCO for observing projects, proprietary periods, the LTA, and authorship, among other policy issues. Please also add the official LOFAR acknowledgement to your papers.
How do I access archival LOFAR data?
This is done via the Long Term Archive. Data observed as part of LOFAR projects becomes public after a proprietary period of 1 year. You can read more details about the LTA and how to use it here.
I have a question that is not covered here!
Please submit a support request at https://support.astron.nl/sdchelpdesk with your question and we will do our best to answer it. If deemed of sufficient general relevance, then it may also be incorporated into this guide in future.
Subscribe to the LOFAR newsletter!
Visit this page and check the subscription section at the bottom!
Subscribe to the LOFAR News mailing list!
By using this form
Useful Links
LOFAR overview: astron.nl/general/lofar/lofar
ASTRON telescopes pages: https://science.astron.nl/telescopes/
LOFAR policies: https://science.astron.nl/telescopes/lofar/lofar-policies/
LOFAR Calendar: goo.gl/3H4rAB
LOFAR wiki: astron.nl/lofarwiki
NorthStar proposal system: lofar.astron.nl/proposal/setUpProposalList.do
LOFAR observation specification tools
MoM: lofar.astron.nl/mom3
TMSS: https://tmss.lofar.eu/login
LOFAR cookbooks: https://support.astron.nl
Long Term Archive: lta.lofar.eu
Long Term Archive manual: astron.nl/lofarwiki/doku.php?id=public:lta_howto
Solved issues: https://science.astron.nl/telescopes/lofar/lofar-system-overview/station-system-status/system-issues/
LOFAR overview paper: https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2013/08/aa20873-12/aa20873-12.html
LOFAR science papers: https://science.astron.nl/telescopes/lofar/science-with-lofar/lofar-papers/
LOFAR slide repository: astron.nl/LofarSlides/index.php
LOFAR tools: https://science.astron.nl/telescopes/lofar/observing-with-lofar/tools/
SDCO contact page: https://science.astron.nl/sdc/submit-a-support-request/
Interactive LOFAR map: https://astron.nl/lofartools/lofarmap.html
Any questions about this guide?
Science Data Center Operations (https://support.astron.nl/sdchelpdesk)